The use of regression models is very common, and serves a very
specific point to us as managers. Regression models allow us to
predict the outcome of one variable from another variable.
Example
We can use a regression model to predict the
mortality of a ponderosa pine tree based on the amount of crown
scorch.
Regression models are very common and you have all probably seen
them used in the scientific literature. Often times regressions
models are associated with a scatter plot, as shown below.
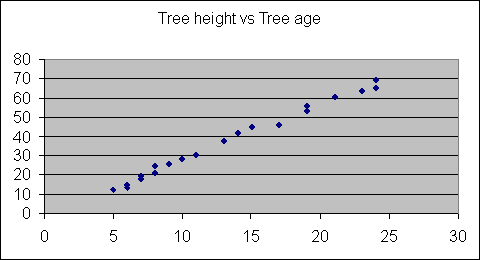
Figure 1. Shows the relationship between tree height and tree age
for species X
We will now add a simple linear regression equation to our example
and calculate the correlation of determination (R2):
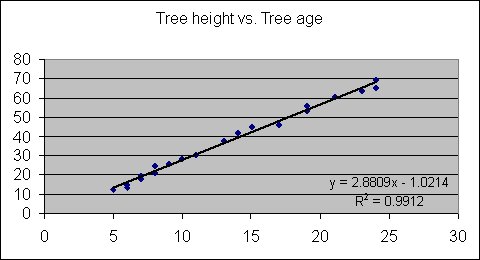
You'll notice on the figure we have identified the statistical equation
which describes the line of best fit and the correlation of
determination identified as R2. Although we will not go over the
details of the correlation of determination you should be aware that
it is essentially a measure of the strength of the linear
relationship between the two variables.
We should note that just because there appears to be a strong
relationship between tree height and tree age the model does not
imply that tree height depends upon tree age, in other words the
model does not show a cause and effect relationship. Great care
should be used when drawing conclusions based on a regression
analysis.
The scatter plot above could be used to build a simple linear
regression model, however we could add more factors to help us
better predict the outcome, these are called multiple regression
models, or we could use some other form of a model that is not
linear in nature, called a non-linear regression model.
Additional Information
Regression Models |
