
The Logit Model
The logit model, which will be discussed again later in the Mode Choice module, has
been used by the Portland, Oregon metropolitan area. The probability of selecting a
particular destination zone is based on the number of trip attractions estimated for that
destination zone, relative to the total attractions in all possible destination zones. The
probability is applied to trip productions estimated for the origin zone, making it
conceptually similar to the gravity model.
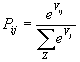
where
Pij= probability of trips from zone i choosing destination j
Vij= Aj-a tij+b t2ij where a and b are parameters to be estimated
Aj=trip attractions estimated for zone j
tij= highway travel time to zone j from zone i
Z= total number of zones
Multiplying the probability of traveling from zone i to zone j by the number of trips
produced by zone i will yield the number of trips produced by zone i that will travel to
zone j.
|