|
Home
4
Targeted Grazing
Prescriptions:
 Forbs
Forbs
 Grasses
Grasses
 Woody Plants
Woody Plants
|
|
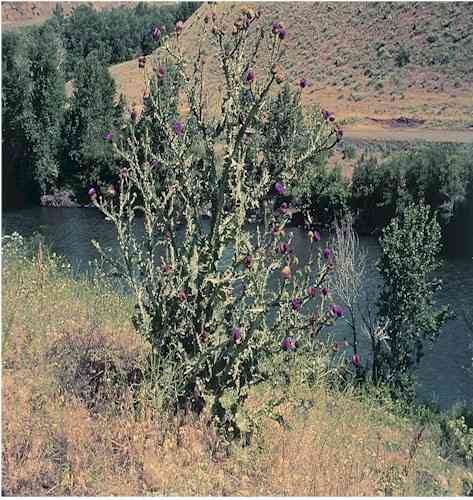
Scotch
Thistle
Onopordum
acanthium |
|
|
|
Description:
Scotch thistle is a tap-rooted, biennial plant
that can grow to 12 feet tall. It reproduces by
seeds. During the first year rosette leaves can
grow to 2 feet long and 1 foot wide. They are
densely covered with fine white hair giving them
a blue-grey color. The edges of the leaves are
very wavy, lobed, and tipped with sharp spines.
A thick, upright stem is produced the second
year. Stem leaves are deeply lobed, spiny, and
alternate. The leaf blades extend along the stem
as wing-like projections. The entire plant is
covered with fine, dense hairs giving it a wooly
appearance. Each branch of the stem produces two
to three large flowerheads about 2 inches in
diameter. Flowers are bright reddish-purple in
color. The seeds are smooth, spatula-shaped, and
tipped with a plume of soft bristles.
|
 |
|
Management Guidelines:
Type and Class of
Livestock:
All classes of sheep, goats, and cattle.
Grazing Objective:
Prevention of flowering and reduction of stem
density.
Growth Stage for
Treatment:
Graze Scotch thistle at the rosette to bolting
stage. Livestock will graze Scotch thistle with
some reluctance, and better results can be
achieved after they have some experience with
the plant. Heavy to severe utilization, using
short-duration, high-intensity grazing
practices, provides the best results when
repeated for several years to deplete the seed
bank.
Potential Effectiveness:
Prescribed grazing of Scotch thistle is
considered an effective means of control,
suppressing flowering and reducing stem density
30 to 50%. Sheep, goat, and cattle grazing is
considered effective, although several years of
grazing may be needed to reduce populations of
Scotch thistle. Maintaining vigorous perennial
grass competition is essential to long-term
management. Grazing Scotch thistle is very
effective when combined with a follow-up
herbicide treatment. |
|
References:
Sullivan, P.G. 2004. Thistle control
alternatives. National Sustainable Agriculture
Information Service. Available at:
http://attra.ncat.org/new_pubs/attra-pub/PDF/thistlecontrol.pdf .
Accessed 03 September 2006
Holst, P.J., C. J. Allan, M.H. Campbell, and A.R.
Gilmour. 2004. Grazing of pasture weeds by goats
and sheep. 1. Nodding thistle (Carduus nutans).
Australian Journal of Experimental
Agriculture 44:547-551. |
|