The last sampling design we will discuss is a stratified random
sampling design. This type of sampling design requires you to divide
the population into subpopulation of a known size.
Example
We could divide a watershed up into vegetation
classes or into treatment blocks. Once the strata are identified at
least two samples will be collected from each strata or
subpopulation.
The advantage of this sampling design is that you can have a more
precise estimation of the population mean compared to a simple
random design of the same size. It may also be beneficial to look at
each subpopulation. For example if each stratum is a different
vegetation type we may have different long term goals and management
tools to consider when treating the population.
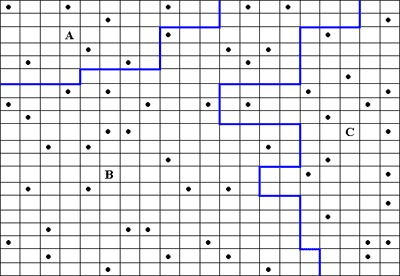
Figure 3. Possible arrangement of 56 samples using a stratified
random sampling method. Notice that the strata are identified by the
blue line and labeled a through c. |
