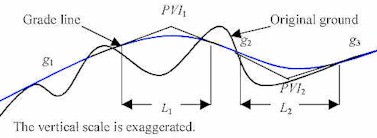
The curves joining the grade lines are called vertical curves, and their function is to
make a smooth transition from one grade to another. Details of designing sag and crest
vertical curves are presented in the chapter "Geometric Design".
During or after completion of the detail base map (see Surveys and Maps), the traffic
engineer prepares a vertical profile of the alignment. Information needed to create a
vertical profile includes the vertical curve data and the elevations of the existing
ground surface along the chosen route. The first step is to draw the existing ground level
along the centerline of the proposed alignment, with elevation data on the vertical scale.
Then draw the centerline of the alignment on the profile, as shown below:
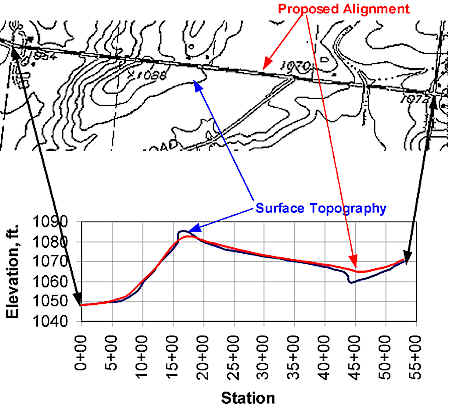
At a minimum, data included with the centerline are the elevation and stations of all
points of intersection and the lengths of vertical curves. The Excel demonstration
provided with this concept uses station notation and elevation information to develop a
vertical crest curve and the accompanying information.