1
. (5 pts) The following statements pertain to the
first-day survey and the discussion of it in the following lectures. Which statements are true? (multiple True/False = MTF)
(A) As discussed in class (and can be inferred from each
statement in the survey), the purpose of this survey was chiefly to assess what
you had already learned about biology.
(B) We discussed various factors that influence peopleÕs
decisions. Some items in our list
were considered emotional factors, and others were considered rational factors,
and some both.
(C) We suggested that a response indicating uncertainty
reflected a lack of knowledge about the statement. Thus someone knowledgeable about the subject would not be
uncertain.
(D) More of the class was willing to consider that
governments had concealed evidence of aliens having landed on earth than was
willing to consider that aliens had landed on earth.
(E) For many statements, classes from previous years had
similar distributions of responses as yours.
Scientific Method
2).
(4 pts) The figure below shows the
steps of the scientific method, labeled (i)-(viii). Which of the following options are true? You are assumed to know the identity of
these steps for this question.
(MTF)
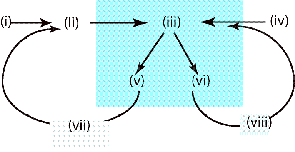
(A) The scientific method needs all 8 steps shown
to be fully functional.
(B) If observations were made to test a model, the
observations would be step (ii)
(C) For a particular model, if the first round of
evaluation enters the (right) loop containing (vi) and (viii), then subsequent
evaluations of that model are no longer able to enter the left loop
(v-vii).
3. (5 pts) Astrologists claim to be able to predict your future
and give insights to your being, and they have well-defined rules to use in
reaching those forecasts, based on your birthday and birth hour. However, there are no attempts to test
the accuracy of those predictions Š no formal observations, no comparisons of
observations to predictions, and no consequent changes in the rules used.
Which elements
of the scientific method are present in the above description? MTF
|
(A)
Goal |
(B)
Model |
(C)
Data |
(D)
Evaluation |
(E)
Revision |
(F)
None |
4. (5 pts) Brad has
two computers of the same model, but one has stopped working recently. He thus decides to use the scientific
method to determine the cause of the failure. He knows how to replace boards and the CPU, so his plan
involves replacing different parts that he thinks could be the source of the
failure. Starting with his first
guess as to which part is broken, he removes the suspect part from the bad
computer and inserts the equivalent part from the good computer. The bad computer does not work. He then returns the parts to their
original computers and repeats the operation for his second guess at the bad
part. The bad computer still does
not work. So those parts also get
returned to their original computers, and he moves to his 3rd guess,
following this same procedure.
Finally, after exhausting his ideas for which part is broken, he has
still not found the part causing the computer to fail. Unknown to him, the bad computer has
two failed parts, and his procedure never replaced more than one part at a
time.
Which elements
of the scientific method are present in the above description? MTF
|
(A)
Goal |
(B)
Model |
(C)
Data |
(D)
Evaluation |
(E)
Revision |
(F)
None |
5. (2
pts). Continuing with the above
problem (4), Brad now realizes the possibility that two parts may be bad. He thus introduces a simple change in
his procedure: instead of putting
the part from the good computer into the bad, he takes the part from the bad
computer and puts it into the good computer (one at a time, as before). He then finds the two bad parts when
the good computer fails at two steps in his procedure.
Which elements
of the scientific method are present in this procedure that were absent
in problem 4? MTF
|
(A)
Goal |
(B)
Model |
(C)
Data |
(D)
Evaluation |
(E)
Revision |
(F)
None |
6.
(4 pts). Jerry and Ken are storm chasers, driving around Texas, Oklahoma, and
Kansas looking for tornadoes in the spring. In the three previous years, their general mode of operation
has been to watch weather maps and weather reports, then drive to locations
where tornadoes are expected. They
have spotted 5 tornadoes this way.
Which elements
of the scientific method are present in the above description? MTF
|
(A)
Goal |
(B)
Model |
(C)
Data |
(D)
Evaluation |
(E)
Revision |
(F)
None |
7.
(5 pts) Which of the following
statements apply to our teachings of the scientific method and to violations of
the scientific method? (MTF)
A) Models and evaluation must be closely tied to goals to
be useful in the scientific method.
B) Simple endeavors, such as those involving the repair
of broken machinery or the writing of an essay are too elementary to represent
(or be a useful model of) the scientific method
C) The Wright BrothersÕ success in making the first
airplane was greatly facilitated by their use of the scientific method.
D) Several social institutions designed to help us
(church, government agencies) are lacking one or more elements the scientific
method.
E) A criminal trial and subsequent judicial procedures
has all elements of the scientific method, although revision is a weak step.
Models
8. (4 pts) Two people are arguing about
whether the structure of DNA as taught and illustrated in textbooks is an exact
chemical model of DNA in cells, regarding structure and function. David
says that the structure as taught is a false model for many reasons, including
the fact that one cannot do genetic manipulations on the textbook model,
cannot do any experiments with it, and furthermore, it does not capture the
complex chemistry in the cell. John says that it is exact because we know beyond
any doubt that the molecule in the cell consists of a twisted, linear string
of bases (A, G, C, T) like the textbook says.
Which of the following options are true as regards this
disagreement. (Consider the italicized phrases in this paragraph to be true.
You donÕt need to know anything about DNA to answer this question,
except that DNA resides in our cells).
One answer only
(A) John is right; David is wrong. The structure
of DNA has been so well documented that what the text says is right, and
therefore, it is an exact model.
(B) David is right, John is wrong. The true complexity of any cell chemistry differs in obvious ways from anything that can be captured on paper, just as the detailed physical and chemical description of a fire is not the same as the fire itself Š all models are false.
(C) They are both correct; each of their statements
refers to a different goal.
9. (5 pts) Demonstrations. Lecture used some
demonstrations and topics to illustrate the scientific method and others to
illustrate models. Indicate which
of the following demos or topics were used to illustrate (some aspects of) models. If a demo or topic was not used in class,
or if it was used to illustrate the scientific method, do not fill it in. MTF
|
(A) Slogans |
(B) Wheel of
fortune game |
(C) Solar
system |
(D) Phone book
and brochure pictures |
(E) Pet
psychics |
10. (4 pts) Mark all statements that specifically illustrate the
concept that there can be more than one model of any particular object or idea
(MTF).
A) Four different versions of each exam are prepared for
the class. Each student gets only
one version, but the grade thresholds are the same for each version.
B) Our government extrapolates from rodents to estimate a
chemicalÕs risk to humans, because the number of people exposed to the chemical
is too few to rely on just human data.
C) All models are false.
11.
(8 pts) General points about
models. Which of the following are
true? MTF
- ACU
(accuracy, convenience, uniformity) refers to the order of preference we
want in the characteristics of a model Š the most useful models are more
accurate than convenient and more convenient than uniform. Thus, you were never told CUA or
UCA.
- Although
the usefulness of a model depends on the goal, the limitations do not
depend on the goal.
- A
precise mathematical model that is properly parameterized (all the terms
have been assigned their correct values) is considered an exact model of
the process it represents.
- A
model CAN be both accurate
and convenient (last yearÕs exam had an option stating otherwise), because
there is nothing that keeps a model from satisfying several of the 3 ACU
criteria.
- One
model can be useful for two or more different goals.
- Our
knowledge is represented by models, and changes in models are consequently
the bases by which we measure progress.
12 (4 pts) Which of the following were described as useful models
of humans for genetics, molecular biology, and other health-related goals (as
noted in class and/or the book)?
MTF
|
A) mice |
B) yeast |
C) bacteria |
D) viruses that attack
bacteria |
E) none |
HIV and Mathematical models in epidemiology
13. (3 pts) From the
Notes and lecture, indicate which of the following points apply to the HIV
lectures? MTF
(A) Accuracy: mathematical models of epidemics are very inaccurate
models of the many biological details of infection and transmission.
(B) HIV biology: this virus follows an unusual pattern of
infection. The concentration of virus in a personÕs blood stays low from the
time of infection until 6 years later.
It is these later years when the person develops antibodies and starts
transmitting the virus.
(C) Risk: For
a group of individuals having sexual encounters with each other, HIV can spread
through most of that group before the first case of AIDS appears.
14.
(4 pts) Which of the following
options address(es) the HIV lectures and reflect the message from those
lectures? MTF
A) An interest rate of (1/365)% compounded daily yields
more money in a year than 1% compounded yearly. (Ignore leap years.)
B) The impact of early transmission versus late
transmission on the spread of an infectious disease is similar to that of
frequent versus infrequent compounding of interest rates on growth of a bank
account.
C) From the model considered in class (and the book),
efforts to control the behavior of individuals only after they became
detectably HIV+ would likely have had little impact on the spread of the HIV
epidemic.
D) The suggestion that early transmission is important to
the spread of HIV still lacks direct observations that determine the
stage of a personÕs infection when they transmitted the virus to someone else.
Condoms
15. (5pts). Why is
the airburst test considered a useful model of sex in testing condoms for the
goals of preventing STD transmission and preventing pregnancy? MTF
A) uniformity
B) accuracy
C) convenience
D) it is a whole-condom measure of integrity
E) it provides a useful measure of STD passage through an
intact condom
16. (5 pts) (MTF) The
conclusion that Ņcondoms reduce rates of HIV transmissionÓ
A) is based on condom performance in mechanical tests
B) is based on volunteer studies in which both partners
are already infected with HIV
C) treats one condom (or condom brand) as a model of
another condom (brand)
D) is based on small differences in HIV transmission
rates observed between strict condom users and strict non- users (there is less
than a 2-fold difference in rates between the two groups).
Extrapolating Health Risks
17.
(4 pts) (MTF)
A MSDS (material safety data sheet)
- is an accepted/useful
model of a chemicalÕs effect on you
- may describe the
effect of a chemical on non-humans
- described only those
consequences of exposure that have been estimated beyond a reasonable
doubt
- lacks a great deal of
potentially useful information
- does not list cancer
risks
18-21.
(4 pts each) One answer per
question. In the cases below,
indicate whether the problem identified in the lecture/book was primarily an
illustration (or example) of
A) extrapolation from high to low dose
B) extrapolation from non-humans to humans
C) extrapolation from one type of hazard to a related
hazard
D) was resolved with actual measurements of the effects
of low doses
E) None of the above
Note: if
(D) applies, then that answer takes precedence over the others.
18. The lethal effect of dioxin in humans: (A) (B)
(C) (D) (E) one answer only
19. Fetal alcohol syndrome and the effect on the fetus
of low levels of alcohol consumed by the mother (e.g., 1 drink/week): (A)
(B) (C) (D) (E) one only
20. The harmful effects of 2nd-hand tobacco
smoke: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) one
only
21. Rodent models of cancer applied to low doses of
substances: (A)
(B) (C) (D) (E) one only
Themes
22. (8 pts) Each of the following options lists or refers to a
theme in the course notes and then offers an explanation of what it means.
Which of these statements about Meaning are true and reflect the theme? (MTF)
A)
Theme: Progress through the
scientific method. Meaning: the scientific method is a cyclic procedure that has
been used to make considerable progress toward goals in many different
settings.
B)
Theme: Progress through the
scientific method. Meaning: the scientific method guarantees that progress will
be made toward goals, because all models are false and thus are certain to be
rejected.
C)
Theme: All models are false. Meaning: we use models for what they have to offer, but there
is no point in trying to find better ones, because none is perfect.
D)
Theme: Pieces and parts as models. Meaning:
ultimately, the greatest success comes from taking things apart (into pieces),
because we can understand the whole only by understanding how it is put
together.
23. (2 pts.) Exam Key Code: Fill in (AB) on question 23 to
indicate your exam code.