

DISTANCE ESTIMATION OF ABUNDANCE
Density is homogeneous within the area surveyed
Density estimation for line transects and circular plots (with perfect detection)
DENSITY =
For line transect
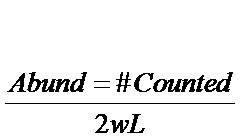
2w = width of transect
L = length of transect
For circular plots
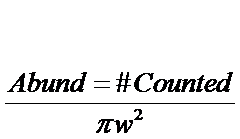
w = radius of plot
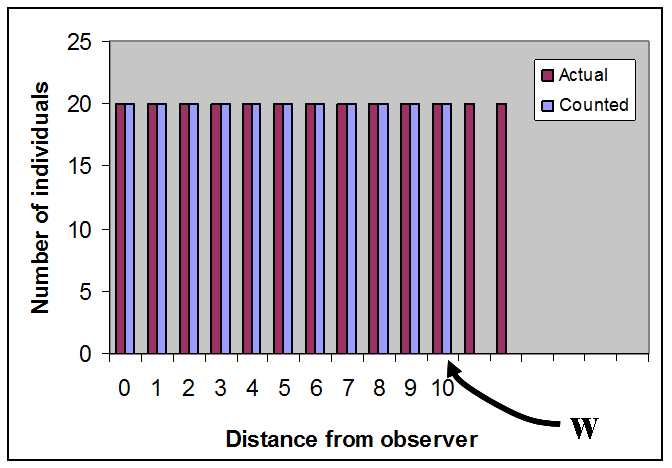
But not all individuals will be detected
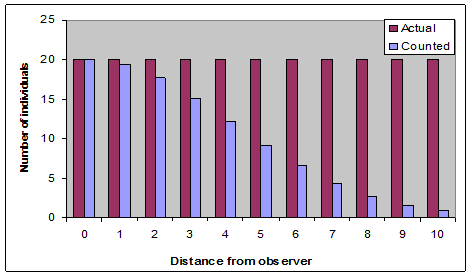
Therefore,
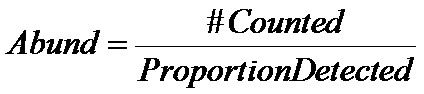
Detection function: g(x) = Probability of observing and individual at given a distance (x) from the observer.
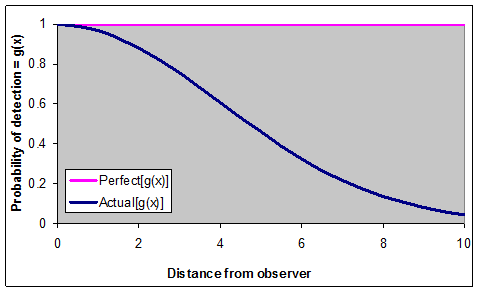
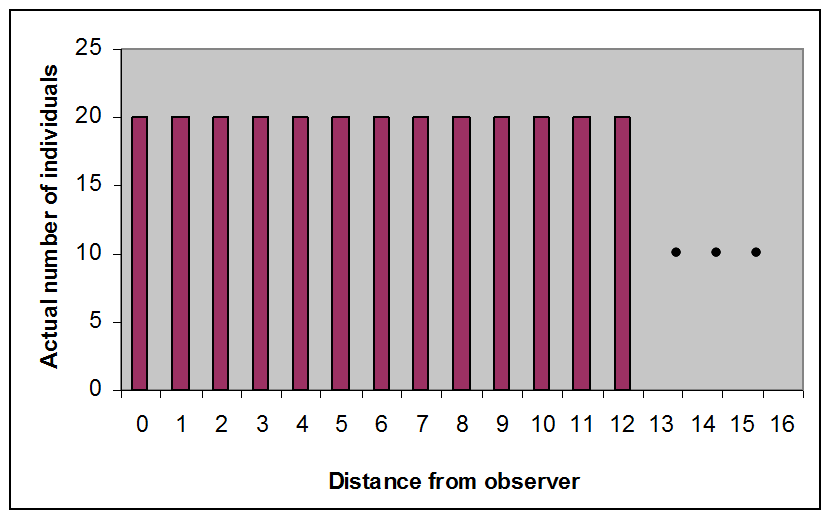
The critical assumption permitting estimation from distance data is that all individuals directly on the line (distance = 0) are detected. So, Actual[g(0)] = 1
If this assumption holds:
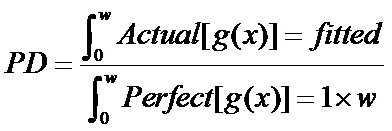
and we can find the area under the actual detection function by fitting to the observed data...
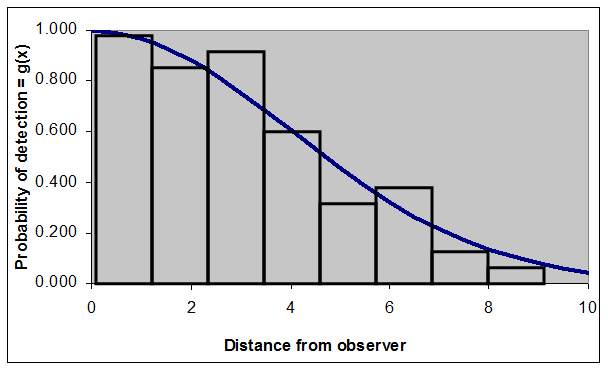
The main problem in distance estimation involves developing an appropriate model for g(x).
There are a variety of models and associated estimators for g(x) that can be fit to the detection-distance data:
- Exponential power series
- Exponential polynomial
- Negative polynomial
- Negative exponential
- Half-normal.
- Uniform
- Fourier series (Uniform with cosine expression)
- Others...
Akaike's Information Criteria can be used to determine the "best" function (model) given the detection-distance data.
Objects directly on the line will never be missed, i.e., g(0) = 1.
Points are fixed at the initial sighting position (i.e., no movement before or after sighting).
Distance and angles are measured accurately.
Sightings are independent events.
Shape criterion: function describing g(x)