|
There are 5 main resources required for the growth and development of terrestrial vegetation (solar energy, carbon dioxide, water, nutrients, and a medium for support).
Of these 5 resources 3 of them are provided by the soil (water, nutrients, and a support medium) (Barnes et al. 1998).
Soil is one of the most important factors influencing the growth of individual plants and the functioning of ecosystems.
Soil is essentially a porous medium consisting of organic matter, water, gasses and minerals.
Soil is produced by the combined influences of weather, topography, biota time, and geological materials (Barnes et al. 1998).
The geological materials which eventually make up soils, called the
parent material, are formed by the weathering process.
Soils are generally defined as the natural, unconsolidated mineral and organic material occurring on the surface of the earth.
Soil parent material include consolidated parent materials such as igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, which formed soil in place, and unconsolidated materials which have been formed by the transportation of the parent material by ice, water, wind, and gravity.
An example of unconsolidated soils can be found in the eastern United States where glaciers have left behind a landscape consisting of almost entirely of unconsolidated materials.
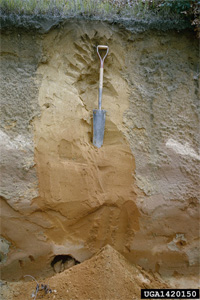
After parent material is formed it becomes differentiated into horizontal layers called the
soil profile.
The development of the soil profile is dependent upon the climate, parent material, plants and animals using the soil, the physiography of the site and time (Barnes et al. 1998).
Phil Crawl, USDA Forest Service, www.forestryimages.org
|
